Blood Pressure Monitor – Surgitech
₱0.99- Arm-Type
- Fully Automatic
COVID-19 Medical Supplies refer to the equipment, devices, and protective materials essential for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of COVID-19. These supplies have been critical in controlling the spread of the virus, treating infected individuals, and protecting healthcare workers and the general public. During the pandemic, the demand for these supplies surged, highlighting their importance in managing public health emergencies.
Key Categories of COVID-19 Medical Supplies
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is designed to protect healthcare workers and individuals from exposure to infectious agents, including COVID-19. Common PPE items include:
– Face Masks:
— Surgical Masks: Disposable masks that protect against droplets and splashes, commonly used by healthcare workers and the public.
— N95 Respirators: Tight-fitting masks that filter out at least 95% of airborne particles, providing a higher level of protection against viruses.
— Cloth Masks: Reusable masks made from fabric, used by the public to reduce the spread of respiratory droplets.
– Face Shields: Transparent plastic shields that cover the face, providing an additional layer of protection, especially when combined with masks.
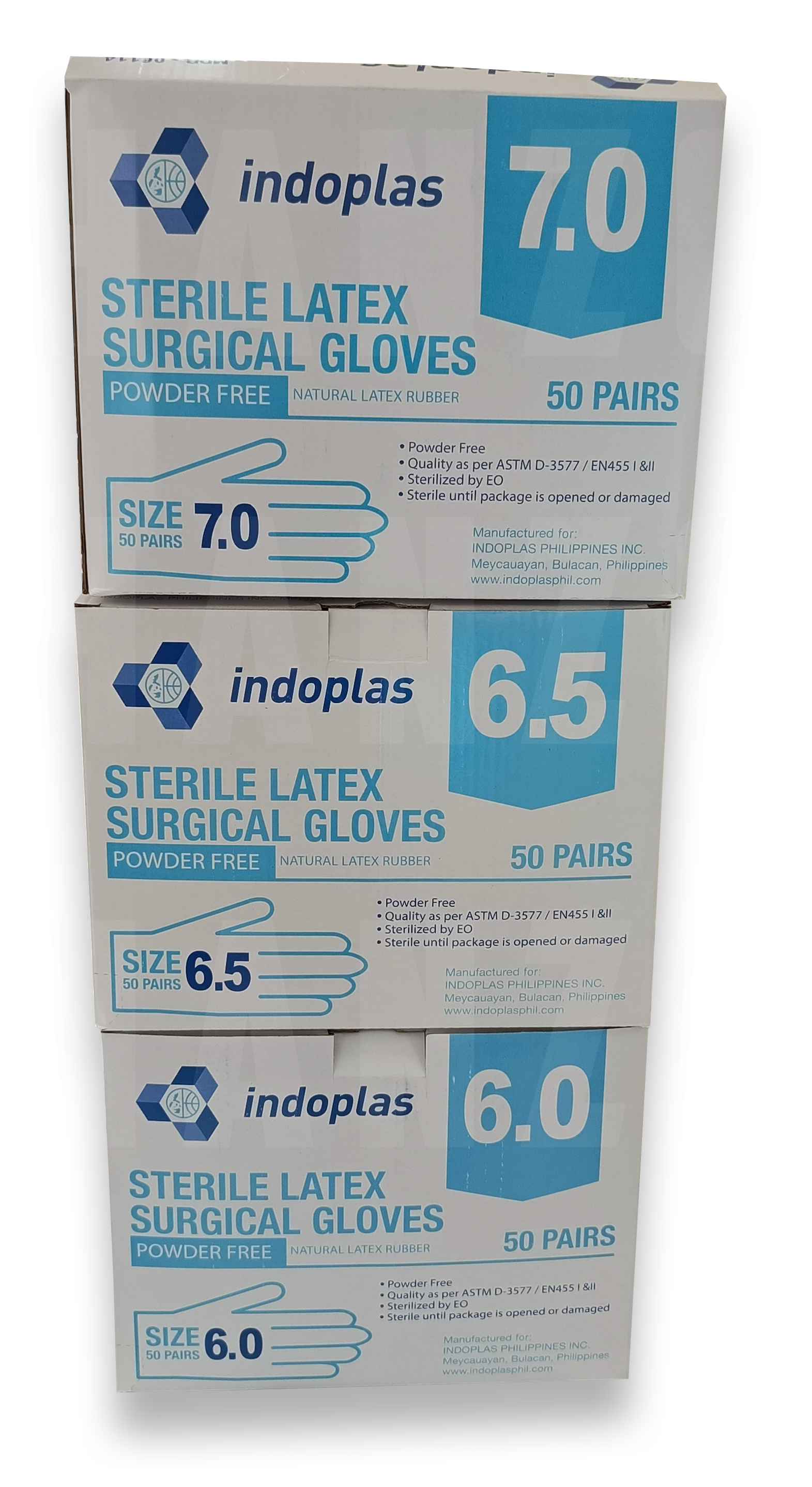
– Gloves: Disposable medical gloves made from latex, nitrile, or vinyl that protect healthcare workers’ hands from coming into contact with infectious materials.
– Gowns: Disposable or reusable gowns made of impermeable materials, worn by healthcare workers to protect against fluids and contaminants.
– Protective Goggles: Eye protection worn in conjunction with masks and face shields to prevent respiratory droplets from coming into contact with the eyes.
2. Diagnostic Testing Supplies
COVID-19 diagnostic testing has been essential in identifying infected individuals and controlling the spread of the virus. Key testing supplies include:
– COVID-19 Test Kits:
— PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Tests: Molecular tests that detect the virus’s genetic material and are considered the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19.
— Antigen Tests: Rapid diagnostic tests that detect specific proteins on the surface of the virus. These tests provide quicker results but are generally less sensitive than PCR tests.
— Antibody Tests: Blood tests that detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the virus, indicating past infection.
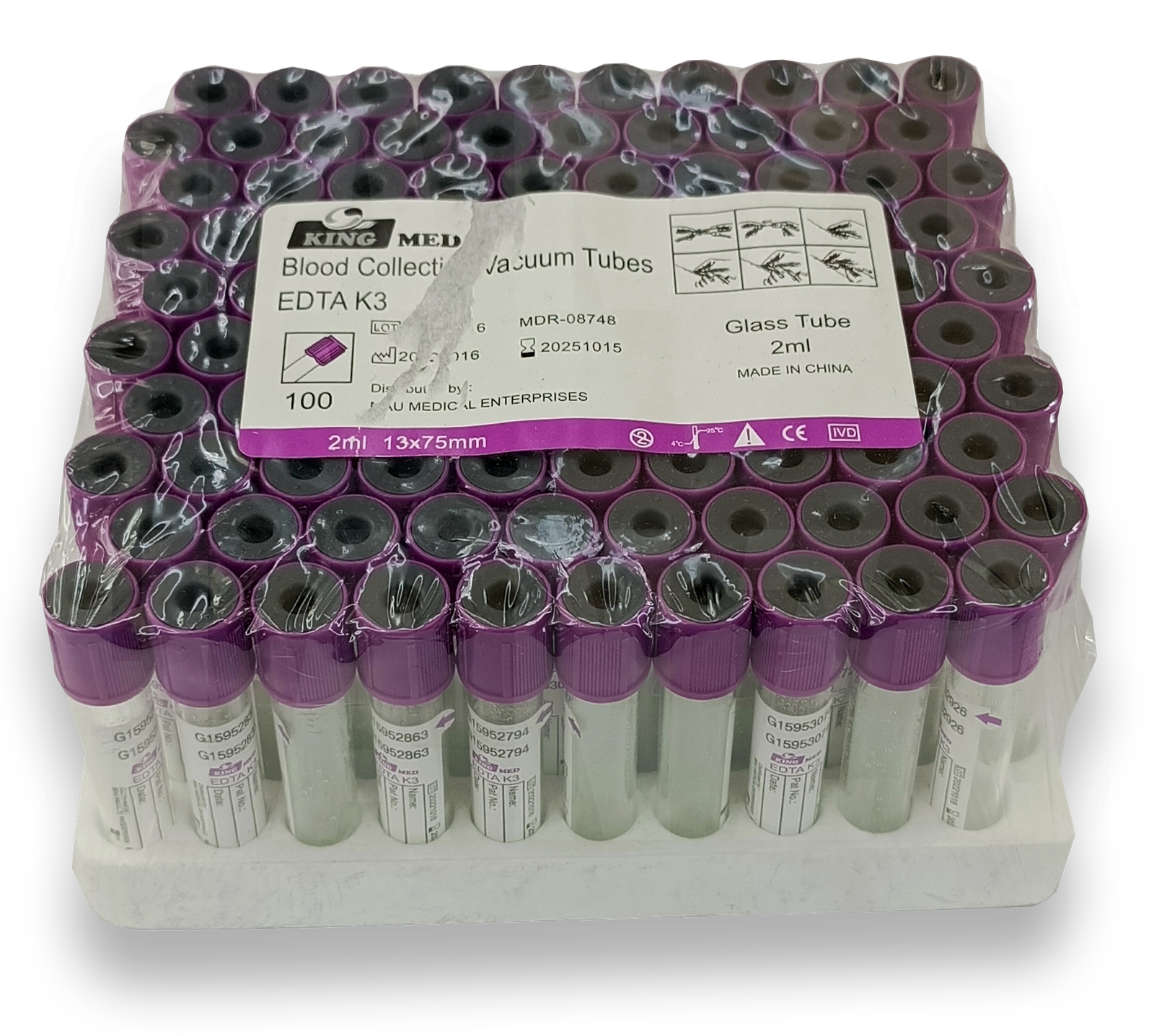
– Swabs: Nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs used to collect samples from the nose or throat for diagnostic testing.
– Specimen Collection Tubes: Vials or tubes that store and transport collected samples to laboratories for testing.
3. Disinfectants and Cleaning Supplies
Cleaning and disinfection play a key role in preventing the spread of COVID-19, especially in healthcare settings and public spaces. Essential disinfectants include:
– Hand Sanitizers: Alcohol-based hand sanitizers (with at least 60% alcohol) that kill viruses on hands when soap and water are not available.
– Disinfectant Wipes: Pre-moistened wipes that contain disinfectant solutions effective against COVID-19 on surfaces.
– Surface Disinfectants: Liquid disinfectants like bleach, hydrogen peroxide, and quaternary ammonium compounds used for cleaning surfaces in healthcare facilities, homes, and public places.
– UV-C Light Devices: Ultraviolet light devices used to disinfect surfaces and air by killing viruses and bacteria, especially in healthcare settings.
4. Medical Equipment for COVID-19 Treatment
COVID-19 treatment, particularly for severe cases, requires specialized medical equipment to manage symptoms and complications such as respiratory distress. Key medical equipment includes:
– Ventilators: Mechanical breathing devices used to assist or take over breathing for patients with severe respiratory failure caused by COVID-19. These machines deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the lungs.
– Oxygen Concentrators: Devices that deliver concentrated oxygen to patients with low blood oxygen levels. They are used in hospitals and home care for patients with moderate respiratory issues.
– Pulse Oximeters: Non-invasive devices that measure oxygen saturation in the blood. These are commonly used to monitor COVID-19 patients’ oxygen levels and determine the need for supplemental oxygen.
– High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC): A respiratory support device that delivers high-flow oxygen therapy to patients with severe respiratory symptoms.
– BiPAP and CPAP Machines: Non-invasive ventilation devices used to help COVID-19 patients breathe by delivering pressurized air through a mask.
5. Vaccination Supplies
With the development of COVID-19 vaccines, vaccination efforts have become a key strategy in controlling the pandemic. Essential vaccination supplies include:
– Syringes and Needles: Single-use syringes and needles for administering COVID-19 vaccines.
– Vaccine Storage Units: Specialized refrigerators and freezers used to store vaccines at the required temperature, particularly for mRNA vaccines that require ultra-cold storage.
– Sharps Containers: Secure containers for the safe disposal of needles and syringes after vaccine administration.
– Vaccine Vials: Single- or multi-dose vials containing COVID-19 vaccines, including mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) and viral vector vaccines (Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca).
6. Isolation and Containment Supplies
These supplies help contain the virus and prevent transmission within healthcare settings and public spaces.
– Isolation Gowns: Worn by healthcare workers when treating COVID-19 patients to prevent the spread of infectious materials.
– Negative Pressure Rooms: Specialized hospital rooms with ventilation systems that prevent contaminated air from escaping, helping to contain airborne pathogens like the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
– Barrier Enclosures: Devices or barriers placed around patients to limit the exposure of healthcare workers to respiratory droplets during procedures like intubation.
7. Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring Tools
To reduce in-person contact and minimize exposure to COVID-19, telemedicine and remote monitoring have become essential parts of healthcare.
– Telemedicine Platforms: Software and hardware systems that allow healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations with patients, reducing the need for in-person visits.
– Remote Monitoring Devices: Devices like remote thermometers, blood pressure monitors, and oximeters that patients can use at home to monitor symptoms and share data with their healthcare providers.
8. Miscellaneous Supplies
Other supplies have been crucial in the management of COVID-19, including:
– Thermometers: Infrared and digital thermometers used to quickly measure body temperature, especially in public spaces like airports or healthcare facilities.
– Barrier Masks and Respirators: Masks designed for high-risk environments, such as FFP2 and FFP3 respirators, offering enhanced protection for healthcare workers.
– Contactless Thermometers: Non-contact infrared thermometers used to screen people for fever in public spaces, reducing the risk of virus transmission through shared devices.
Importance of COVID-19 Medical Supplies
1. Infection Prevention: PPE and disinfectants help prevent the spread of COVID-19, particularly in healthcare settings where exposure risk is high.
2. Timely Diagnosis: Testing supplies, such as PCR and antigen test kits, allow for early detection and isolation of infected individuals, helping to contain outbreaks.
3. Effective Treatment: Medical equipment like ventilators, oxygen concentrators, and pulse oximeters are critical for managing severe COVID-19 cases and saving lives.
4. Vaccination Rollout: Syringes, needles, and storage units are essential for the mass distribution and administration of COVID-19 vaccines, which are key to controlling the pandemic.
5. Remote Healthcare: Telemedicine tools and remote monitoring devices have allowed healthcare providers to continue treating patients while minimizing the risk of virus transmission.
Conclusion
COVID-19 Medical Supplies have played a crucial role in the global response to the pandemic. From personal protective equipment to diagnostic tools and treatment devices, these supplies have been essential in preventing the spread of the virus, diagnosing infections, and treating patients. As the pandemic continues, the availability and proper use of these supplies remain critical to controlling COVID-19 and protecting public health.
Showing 1–16 of 22 results